|
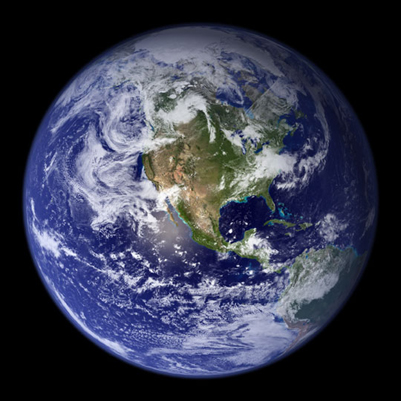
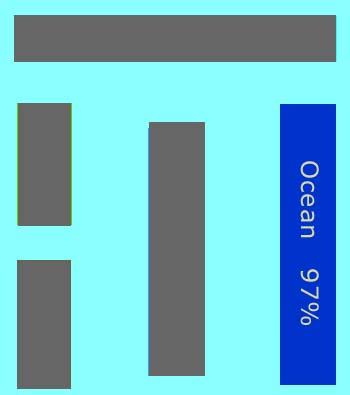
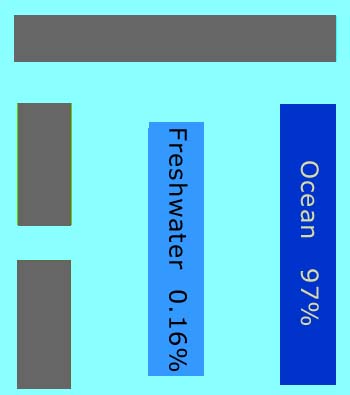
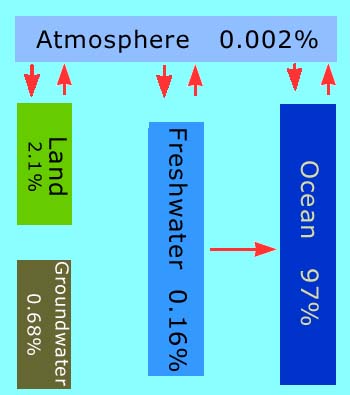
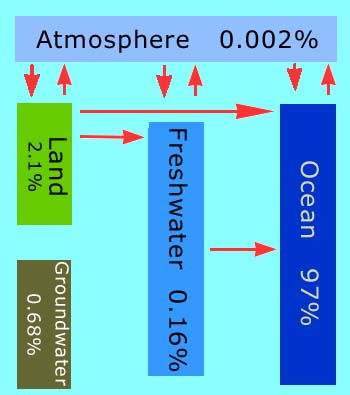
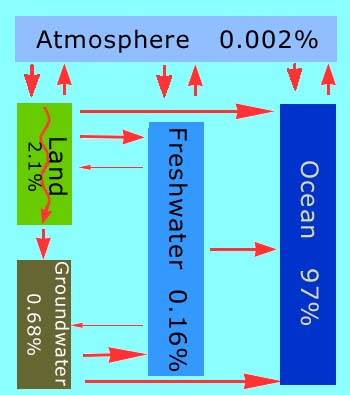
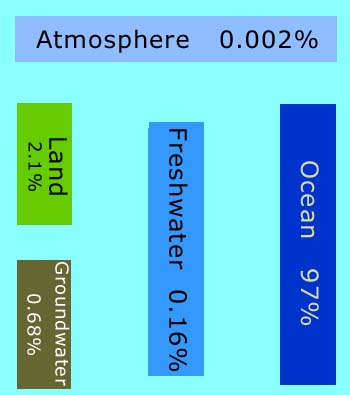
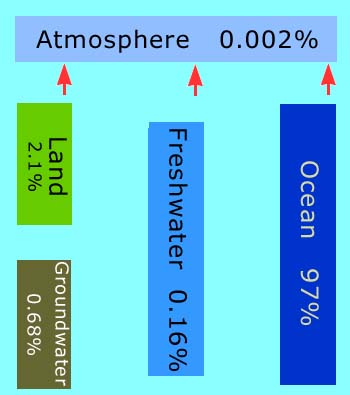
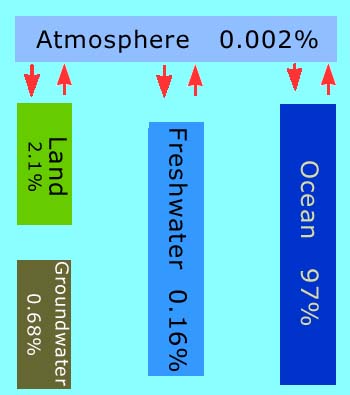
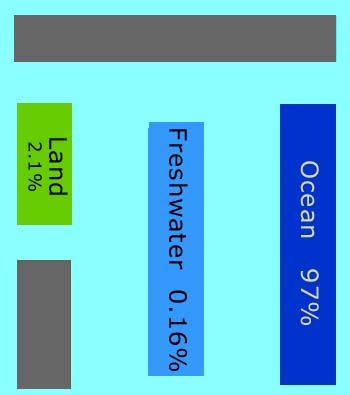
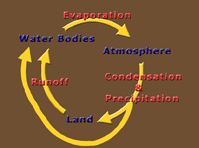
In this view of Earth from space, it is clear that water is an important part of our planet. Seventy percent of Earth's surface is covered by water, and water droplets in the form of clouds can be seen swirling above the surface. This water is in constant motion.
|